3D Modelling Basics
-
Home
-
3D Modelling Basics
3D Modelling Basics
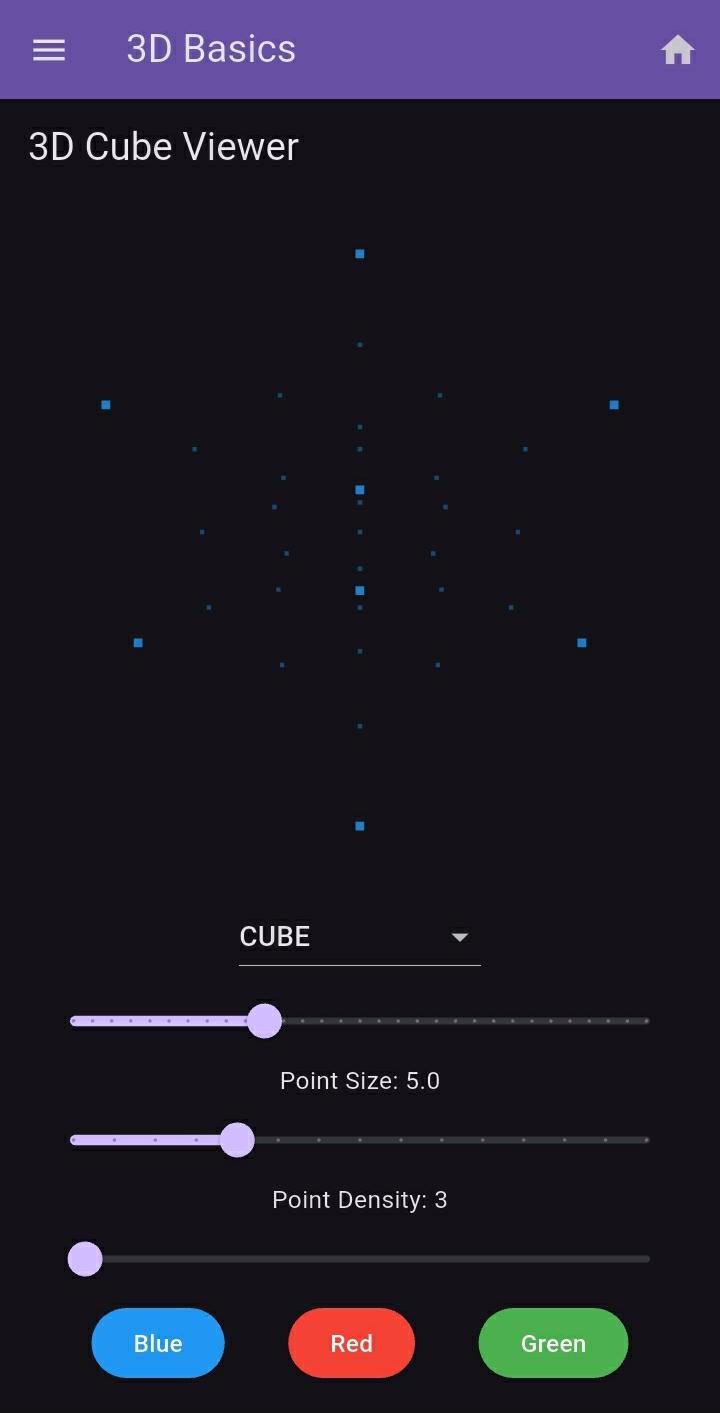
The Hidden Language of Shape
From the simple cube to the complex dodecahedron, geometric shapes contain within them profound mathematical truths that transcend their physical representations. These Platonic solids and everyday objects exist not just in our three-dimensional space, but in a rich multidimensional framework that governs their properties and relationships.
The Fourth Dimension: Time and Transformation
When we animate these shapes, we introduce the crucial fourth dimension of time. This allows us to observe:
The continuous transformation of polyhedra as they rotate in virtual space
How different faces and edges relate to each other through motion
The dynamic interplay between vertices that appears static in traditional models
This temporal dimension reveals the inherent symmetries and structural relationships that define each form's essence.
The Fifth Dimension: Probability and Point Clouds
The point-based rendering technique suggests a deeper truth about material reality:
Each point represents a possible atomic position in a crystal lattice
The density variations mirror electron probability distributions
The transitions between shapes model phase changes in materials
This probabilistic approach moves us beyond rigid edges into a quantum understanding of form.
The Sixth Dimension: Parametric Space
The adjustable parameters create a multidimensional design space where:
Size variations represent scaling operations in manufacturing
Color changes indicate different material properties
Density adjustments model structural integrity at different resolutions
This parametric control lets us explore not just individual objects, but entire families of related forms.
The Seventh Dimension: Topological Relationships
The collection of shapes demonstrates profound topological connections:
The tetrahedron as the fundamental building block
The cube and octahedron as dual polyhedra
The icosahedron and dodecahedron's golden ratio proportions
Everyday objects like cups and plates as practical deformations of ideal forms
These relationships form a network of geometric transformations that hint at higher-dimensional symmetries.
Why This Matters
Understanding shapes through this multidimensional lens enables:
Advanced materials design through geometric principles
Architectural innovation using parametric modeling
Manufacturing optimization via digital twins
Scientific visualization of complex molecular structures
From the atomic to the cosmic scale, these geometric archetypes reappear throughout nature, suggesting they represent fundamental patterns in the fabric of reality itself. By manipulating them in virtual space, we gain intuition about relationships that transcend our normal perceptual limits.
The simple act of rotating a digital icosahedron or adjusting a cup's point density becomes a meditation on the hidden order underlying visible reality - an order written in the language of multidimensional geometry.
Share this service: